#10 C++ 복사생성자
1. 객체 전달과 참조
1.1 값에 의한 호출로 객체 전달 (복습)
함수를 호출하는 쪽에서 객체전달 (1)
함수의 매개변수 객체 생성 (2)
호출하는쪽의 객체가 매개변수 객체에 그대로 복사된다.(3)
⇒ 따라서 매개변수 객체의 생성자는 실행되지 않는다!
1.1.1 값에 의한 호출 방식으로 increase(Circle c)함수가 호출되는 과정
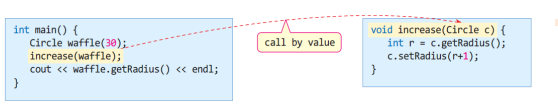
아래의 예시에서 생성자, 소멸자 순서를 나열해보면,
- waffle생성
c(매개변수 객체)의 생성자 실행되지 않음.<= 호출되는 순간의 객체상태를 매개변수 객체에 그대로 전달하기 위함.c(매개변수 객체)의 소멸자 호출← 매개변수 객체의 생성자, 소멸자의 비대칭 실행구조.- waffle소멸
class Circle {
int radius;
public:
Circle(int r) : radius(r) {}
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int r) { radius = r; }
};
void increase(Circle c) { //매개변수 객체 c생성(3) (하지만 생성자는 실행되지않는다!)
// 매개변수로 객체 c가 생성된다.
// 이 경우 c는 값에 의한 호출로 생성된 복사본 객체이다.
// 복사 생성자가 실행되며, 호출된 객체의 상태를 그대로 복사한다.
int r = c.getRadius(); // c 객체의 반지름 값을 가져온다.
c.setRadius(r + 1); // c 객체의 반지름을 1 증가시킨다.
} // 원본 객체에는 영향을 미치지 않는다<---------------------------------중요
int main() {
Circle waffle(30); //(1) waffle객체를 생성한다.
increase(waffle); //(2) 값에 의한 호출로 waffle 객체의 복사본을 increase 함수에 전달
cout << waffle.getRadius() << endl;
// waffle 객체의 반지름 출력. increase 함수에서 변경된 값은 원본에 반영되지 않음.
return 0;
}
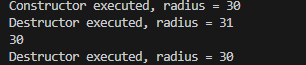
출력결과 1이 증가하지 않은 값이 출력됨
1.1.2 값에 의한 호출 예제코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath> // atan2 값을 호출할 때 이것 필요함
using namespace std;
class Circle5
{
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle5();
Circle5(int r);
~Circle5();
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int radius) { this -> radius = radius;
}
};
Circle5::Circle5()
{
radius = 1;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::Circle5(int radius)
{
this->radius = radius;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::~Circle5()
{
cout << "Destructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
void increase(Circle5 c)
{
int r = c.getRadius();
c.setRadius(r + 1);
}
/*이름이 같지만 매개변수의 타입 다르다.*/
void increase(Circle5 *c) //매개변수 포인터
{
int r = (*c).getRadius();
(*c).setRadius(r + 1);
}
int main()
{
Circle5 waffle(30);
increase(waffle); //----> 값에 의한 호출
cout << waffle.getRadius() << endl;
return 0;
}
1.2 주소에 의한 호출로 함수에 객체 전달

- 함수 호출시 객체의
주소만전달한다. 함수의 매개변수는 객체에 대한 포인터 변수로 선언한다.- 즉, 주소에 의한 호출시, 매개변수로 전달되는것은 객체의 주소일 뿐이므로, 새로운 객체가 생성되지 않는다.
1.2.1 주소에 의한 호출로 increase(Circle *p)함수가 호출되는 과정
void increase(Circle *p) { //매개변수 포인터 p생성(3)
int r = p->getRadius();
p->setRadius(r + 1);
}
int main() {
Circle waffle(30); //waffle객체 생성 (1)
increase(&waffle); //waffle의 주소가 p에 전달(2) (주소에 의한 호출)
cout << waffle.getRadius() << endl;
}
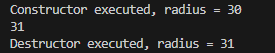
출력결과 1이 증가한 값이 출력됨
1.2.2 주소에 의한 예제코드
class Circle5
{
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle5();
Circle5(int r);
~Circle5();
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int radius) { this -> radius = radius;
}
};
Circle5::Circle5()
{
radius = 1;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::Circle5(int radius)
{
this->radius = radius;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::~Circle5()
{
cout << "Destructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
void increase(Circle5 c)
{
int r = c.getRadius();
c.setRadius(r + 1);
}
/*이름이 같지만 매개변수의 타입 다르다.*/
void increase(Circle5 *c) //매개변수 포인터
{
int r = (*c).getRadius();
(*c).setRadius(r + 1);
}
int main()
{
Circle5 waffle(30);
increase(&waffle); //----> 주소에 의한 호출
cout << waffle.getRadius() << endl;
return 0;
}
2. 객체 리턴
2.1 객체 리턴이란?
- 함수가 객체(클래스의 인스턴스)를 반환하는 것.
- 반환된 객체는 호출한 쪽에서 새롭게 복사본으로 사용된다.
2.2 동작 원리
- 함수 내부에서 객체가 생성된다.
- 함수가 종료될 때 해당 객체의 복사본이 반환된다.
- 반환된 객체는 원본과 독립적으로 작동한다.
2.3 간단한 예시
Circle getCircle() {
Circle tmp(30); // 반지름 30인 객체 생성
return tmp; // tmp의 복사본 반환
}
int main() {
Circle c = getCircle(); // tmp 객체의 복사본을 c에 저장
cout << c.getArea() << endl;
cout << c.getArea() << endl; // 2826 출력 (반지름 30의 면적)
return 0;
}
3. 참조에 의한 호출로 객체에 참조전달
3.1 참조에 의한 호출의 동작 원리
- 매개변수로 객체의 참조를 전달하여 원본 객체를 직접 조작.
- 새로운 객체가 생성되지 않으므로 복사 생성자가 호출되지 않음.
- 함수가 종료된 후에도 변경 사항이 원본 객체에 반영됩니다.
void increaseCircle(Circle &c) {
int r = c.getRadius();
c.setRadius(r + 1); // 반지름을 1 증가
}
int main() {
Circle waffle(30); // 반지름 30인 객체 생성
increaseCircle(waffle); // 참조에 의한 호출로 원본 객체 수정
cout << waffle.getRadius() << endl; // 반지름 31 출력
return 0;
}
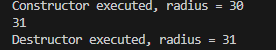
3.2 참조에 의한 호출 코드 예시
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath> // Required for atan2
using namespace std;
class Circle5
{
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle5();
Circle5(int r);
~Circle5();
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int radius) { this->radius = radius; }
};
Circle5::Circle5()
{
radius = 1;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::Circle5(int radius)
{
this->radius = radius;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::~Circle5()
{
cout << "Destructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
// Using reference for the parameter
void increase(Circle5 &c)
{
int r = c.getRadius();
c.setRadius(r + 1);
}
int main()
{
Circle5 waffle(30);
increase(waffle); // Reference to the original object is passed
cout << waffle.getRadius() << endl; // Original object is modified
return 0;
}
실습 8-1 (중요)
2개의 Circle 객체를 교환하는 swap함수를 참조에 의한 호출(call by reference)가 되도록, 작성하고 호출하는 프로그램을 작성하라.
class Circle {
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle() { radius = 1; }
Circle(int radius) { this->radius = radius; }
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
};
**<실행 예시="">**
A의 면적 = 17.27 B의 면적 = 28.26
A의 면적 = 28.26 B의 면적 = 17.27
풀이
**class Circle5
{
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle5();
Circle5(int r);
~Circle5();
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int radius) { this -> radius = radius;
}
};
Circle5::Circle5()
{
radius = 1;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::Circle5(int radius)
{
this->radius = radius;
cout << "Constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
Circle5::~Circle5()
{
cout << "Destructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}**
/*실습 8-1*/
//C는 A의 또 다른 이름이다.
//객체를 새로 만드는것이 아니다.
void Swap(Circle5& C, Circle5& D) /
{
Circle5 tmp = C;
C= D;
D= tmp;
}
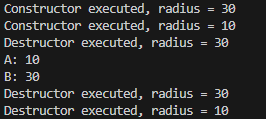
void main()
{
Circle5 A(30), B(10);
Swap(A, B); //참조에 의한 호출
cout <<"A: "<<A.getRadius()<<endl;
cout <<"B: "<<B.getRadius()<<endl;
}
실습 8-2 - 중요
키보드로부터 반지름 값을 읽어 Circle객체에 반지름을 설정하는 전역함수인 read Radius()함수를 구현하여 전체 프로그램을 완성하시오
class Circle {
int radius;
public:
Circle() { radius = 1; }
Circle(int radius) { this->radius = radius; }
void setRadius(int radius) { this->radius = radius; }
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
};
int main() {
Circle donut;
readRadius(donut);
cout << "donut의 면적 = " << donut.getArea() << endl;
}
**<실행 예시="">**
정수 값으로 반지름을 입력하세요 >> 3
donut의 면적 = 28.26
풀이
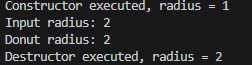
void readRadius(Circle5 &cir) { //이제부터 cir은 donut객체의 별명이다
cout << "input:";
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
cir.setRadius(tmp);
}
int main(void) {
Circle5 donut; // 기본 생성자를 사용하여 Circle5 객체 donut 생성
//참조에 의한 호출 사용
readRadius(donut); // donut 객체의 반지름 값을 설정하기 위해 readRadius 호출
cout << donut.getRadius() << endl; // donut 객체의 반지름 값을 출력
return 0;
}
4. 복사생성자
4.1 얕은 복사와 깊은 복사
4.1.0 얕은복사, 깊은복사
얕은복사
void ex1031_1()
{ // 얕은 복사
int *A = new int[10];
int *B;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
A[i] = i * 10;
}
B = A; // 얕은 복사, 메모리 주소를 공유
delete[] A;
}
깊은복사
void ex1031_2()
{ // 깊은 복사
int *A = new int[10];
int *B;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
A[i] = i * 10;
}
B = new int[10]; // 깊은 복사
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
B[i] = A[i]; // 주소 값에 있는 내용물을 직접 복사해줌
}
delete[] A;
}
4.1.1 얕은 복사
-
객체 복사시, 객체의 멤버를 1:1로 복사
-
객체의 멤버 변수에 동적 메모리가 할당된 경우,
사본은 원본객체가 할당받은 메모리를 공유하는 문제가 발생한다.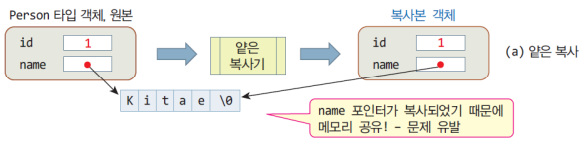
class ShallowCopy { char* data; public: ShallowCopy(const char* str) { // 생성자 data = new char[strlen(str) + 1]; strcpy(data, str); } ******************************************************************************** ShallowCopy(const ShallowCopy& obj) { // 디폴트 복사 생성자 (얕은 복사) data = obj.data; // 포인터 주소만 복사 } ******************************************************************************** void print() { cout << data << endl; } ~ShallowCopy() { delete[] data; } // 소멸자 }; int main() { ShallowCopy obj1("Hello"); // obj1 생성 ShallowCopy obj2 = obj1; // obj2 생성 (얕은 복사) obj1.print(); // 출력: Hello obj2.print(); // 출력: Hello // 얕은 복사의 문제 발생: 두 객체가 같은 메모리를 공유 return 0; // obj2와 obj1의 소멸자에서 동일 메모리를 해제하려고 시도하여 오류 발생 }
4.1.2 깊은 복사
-
객체 복사시, 객체의 멤버를 1:1로 복사
-
객체의 멤버변수에 동적메모리가 할당된 경우,
- 사본은 원본이 가진 메모리 크기만큼
별도로 동적할당 - 원본의 동적 메모리에 있는 내용을 사본에 복사
- 사본은 원본이 가진 메모리 크기만큼
-
완전한 형태의 복사
-
사본과 원본은
메모리를 공유하는 문제 없음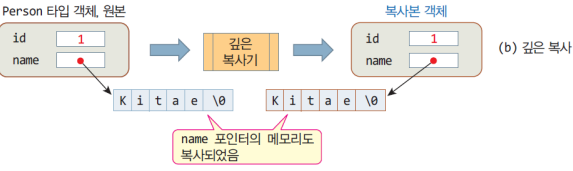
-
class DeepCopy {
char* data;
public:
DeepCopy(const char* str) { // 생성자
data = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(data, str);
}
********************************************************************************
DeepCopy(const DeepCopy& obj) { // 깊은 복사 생성자
data = new char[strlen(obj.data) + 1]; // 새로운 메모리 공간 할당
strcpy(data, obj.data); // 문자열 복사
}
********************************************************************************
void print() { cout << data << endl; }
~DeepCopy() { delete[] data; } // 소멸자
};
int main() {
DeepCopy obj1("Hello"); // obj1 생성
DeepCopy obj2 = obj1; // obj2 생성 (깊은 복사)
obj1.print(); // 출력: Hello
obj2.print(); // 출력: Hello
return 0; // 두 객체의 소멸자가 각각 독립적으로 메모리를 해제하므로 오류 없음
}
4.2 객체간의 초기화와 대입
- 같은 클래스의 객체간에 서로 초기화나 대입이 가능하다.
4.2.1 객체간의 초기화: 복사생성자 이용
-
같은 클래스의 다른 객체와 같은 값을 갖도록 초기화
-
클래스의 멤버 변수를 1대1로 초기화

4.2.2 객체간의 대입: 대입연사자 이용
-
같은 클래스의 다른 객체의 값을 대입
-
클래스의 멤버변수를 1대1로 대입

4.3 복사생성자
복사 생성자 (Copy Constructor)란?
-
정의:
- 객체를 복사할 때 호출되는 특별한 생성자.
같은 클래스의 객체를 이용해서 초기화하는 생성자
-
특징:
한 클래스에 **오직 1개**만 선언가능.- 모양:
클래스에 대한 참조 매개변수를 가지는독특한 생성자
4.3.1 복사 생성자의 원형 (중요)
Circle(const Circle& c); Circle(Circle& c);4.3.2 복사 생성자 호출 방법
Circle c1; // 기본 생성자 호출 Circle c2 = c1; // 복사 생성자 호출 (할당 방식). c1객체를 복사하여 c2에 Circle c3(c1); // 복사 생성자 호출 (직접 초기화 방식) c1객체를 복사하여 c3에4.3.3 클래스 선언 및 구현 요약
class Circle { public: // 복사 생성자 선언 Circle(const Circle& c); // 추가 생성자와 메서드 ... }; // 복사 생성자 구현 Circle::Circle(const Circle& c) { }
4.3.4 복사 생성자 선언 및 구현1
class Circle {
private:
int radius;
public:
// 기본 생성자
Circle(int r = 0) : radius(r) {}
// 복사 생성자
Circle(const Circle& c) {
radius = c.radius; // 기존 객체의 데이터 복사
cout << "Copy Constructor Called" << endl;
}
int getRadius() const { return radius; }
};
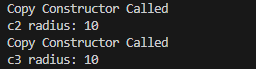
int main() {
Circle c1(10); // 반지름 10인 객체 생성
// 복사 생성자 호출 (방법 1: 직접 초기화)
//c1 객체를 복사하여 c2객체에
Circle c2 = c1; // <-
cout << "c2 radius: " << c2.getRadius() << endl;
// 복사 생성자 호출 (방법 2: 함수 반환)
//c1 객체를 복사하여 c3객체에
Circle c3(c1); // <-
cout << "c3 radius: " << c3.getRadius() << endl;
return 0;
}
4.3.4 복사 생성자 선언 및 구현2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Circle {
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle() { radius = 1; } // 기본 생성자
Circle(int radius) { this->radius = radius; } // 매개변수 있는 생성자
Circle(const Circle& c) { // 복사 생성자
this->radius = c.radius;
cout << "Copy constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
};
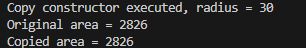
int main() {
Circle src(30); // 반지름 30인 객체 src 생성
Circle dest(src); // src 객체를 복사하여 dest 객체 생성
cout << "원본의 면적 = " << src.getArea() << endl; // src의 면적 출력
cout << "사본의 면적 = " << dest.getArea() << endl; // dest의 면적 출력
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Circle {
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle() { radius = 1; } // 기본 생성자
Circle(int radius) { this->radius = radius; } // 매개변수 있는 생성자
Circle(const Circle& c) { // 복사 생성자
this->radius = c.radius;
cout << "Copy constructor executed, radius = " << radius << endl;
}
double getArea() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; }
};
int main() {
Circle src(30); // 반지름 30인 객체 src 생성
Circle dest(src); // src 객체를 복사하여 dest 객체 생성
cout << "Original area = " << src.getArea() << endl; // src의 면적 출력
cout << "Copied area = " << dest.getArea() << endl; // dest의 면적 출력
return 0;
}
4.4 디폴트 복사 생성자
4.4.1 디폴트 복사 생성자란?
개발자가 클래스에 복사 생성자를 작성해놓지 않으면
- 컴파일러가 자동으로 디폴트 복사 생성자 만들어서 삽입
현재 복사 생성자가 없음
class Circle {
int radius;
public:
Circle(int r);
double getArea();
};
/*메인함수*/
Circle dest(src); // 복사 생성
// Circle(Circle& c) 호출
복사생성자가 없는 컴파일 오류일까?
⇒ 컴파일이 자동으로 아래와 같은 디폴트 복사생성자를 생성한다.
Circle::Circle(Circle& c) {
this->radius = c.radius;
// 원본 객체 c의 각 멤버를 현재 멤버에 복사한다.
}
4.4.2 디폴트 복사 생성자 사례
- 현재 복사생성자가 없는 Book클래스
class Book {
double price; // 가격
int pages; // 페이지수
char *title; // 제목
char *author; // 저자 이름
public:
Book(double pr, int pa, char* t, char* a);
~Book();
};
컴파일러가 삽입하는 디폴트 복사 생성자
Book(Book& book) {
this->price = book.price;
this->pages = book.pages;
this->title = book.title;
this->author = book.author;
}
4.5 얕은 복사 생성자를 사용하여 프로그램이 비정상 종료되는 경우
예시코드
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Person { // Person 클래스 선언
int id;
char* name;
public:
Person(int id, char* name); // 생성자
~Person(); // 소멸자
void changeName(char* name); // 이름 변경
void show() { cout << id << ", " << name << endl; }
****************************************************************************
// 디폴트 복사 생성자 <------------------------------(얕은 복사 수행)
Person(const Person& p) {
this->id = p.id;
this->name = p.name; // 얕은 복사: name 포인터의 주소만 복사
}
****************************************************************************
};
// 생성자
Person::Person(int id, char* name) {
this->id = id;
int len = strlen(name); // name의 문자 개수
this->name = new char[len + 1]; // name 문자열 공간 할당
strcpy(this->name, name); // name 문자열 복사
}
// 소멸자
Person::~Person() {
if (name != NULL) // 동적 할당된 메모리 해제
delete[] name;
}
// 이름 변경
void Person::changeName(char* name) {
if (strlen(name) > strlen(this->name)) return; // 이름 길이 초과 시 변경 불가
strcpy(this->name, name);
}
int main() {
Person father(1, "Kitae"); // (1) father 객체 생성
****************************************************************************
Person daughter(father); // (2) daughter 객체 복사 생성, 복사생성자 호출
// 복사 생성자에서 얕은 복사가 수행되어 father와 daughter의 name 포인터가 동일한 주소를 가리킴.
*******************************************************************************
cout << "After creating the daughter object ---" << endl;
father.show(); // (3) father 객체 출력
daughter.show(); // (3) daughter 객체 출력
daughter.changeName("Grace"); // (4) daughter 이름을 "Grace"로 변경
// daughter의 name 포인터를 통해 동일한 메모리를 수정하므로,
// father.name도 "Grace"로 변경된 것처럼 보이게 됨.
cout << "--- After changing the daughter's name to Grace ---" << endl;
father.show(); // (5) father 객체 출력
daughter.show(); // (5) daughter 객체 출력
return 0; // (6), (7) daughter, father 객체 소멸
// 1. daughter 객체의 소멸자가 호출되어 name에 할당된 메모리 해제.
// 2. father 객체 소멸자 호출 시 이미 해제된 name 포인터를 다시 해제하려고 시도.
// 이로 인해 double free 오류가 발생하며 프로그램이 비정상 종료됨.
}
4.5.1 문제 발생 지점과 원인
디폴트 복사 생성자는 얕은 복사를 수행한다.
name 포인터의 주소만 복사되므로, 두 객체가 동일한 메모리 공간을 참조하게 된다.
-
복사 생성자 (Person(const Person& p))
복사 생성자가 얕은 복사를 수행하므로, father와 daughter 객체가 동일한 name 메모리 주소를 가리키게 된다.즉, father.name과 daughter.name이 같은 메모리를 공유하는 상태가 된다.
-
changeName 호출
daughter.changeName(“Grace”)를 호출하면,
name 포인터가 가리키는 메모리의 내용을 수정한다.하지만 이 메모리를 father 객체도 공유하고 있으므로, father.name의 값도 변경된 것처럼 보이게 된다. -
소멸자 (~Person())
main 함수가 종료되면서 daughter 객체가 먼저 소멸되고, name에 할당된 메모리를 해제한다.
이후 father 객체가 소멸될 때, 이미 해제된 name 메모리를 다시 해제하려고 시도한다.이로 인해 double free 오류가 발생하며, 프로그램이 비정상 종료된다.
4.5.2 해결 방안
깊은 복사 생성자 구현- 새로운 메모리를 할당하여 복사한 객체가 원본 객체와 독립적으로 동작하도록 한다.
- 포인터 멤버 변수를 가지는 클래스에서 필수적으로 구현해야 한다.
Person(const Person& person) {
this->id = person.id; // id 복사
int len = strlen(person.name); // name의 문자 개수 계산
this->name = new char[len + 1]; // 새로운 메모리 공간 할당
strcpy(this->name, person.name); // 문자열 복사
}
- 복사 생성자가 호출되는 상황
- 값에 의한 호출: 함수 매개변수로 객체를 전달할 때.
- 객체 리턴: 함수에서 객체를 반환할 때.
- 객체 초기화: 한 객체를 사용해 다른 객체를 초기화할 때
4.6 (참고) 묵시적 복사생성에 의해 복사 생성자가 자동 호출되는 경우
class Person {
int id;
char* name;
// 정적 메서드를 통해 복사 생성자 호출 시 로그 출력
static void logCopyConstructor(const char* copiedName) {
cout << "Default copy constructor executed for name: " << copiedName << endl;
}
public:
// 기본 생성자
Person(int id, const char* name) {
this->id = id;
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy(this->name, name);
cout << "Parameterized constructor executed, id: " << id << ", name: " << name << endl;
}
// 디폴트 복사 생성자 호출 시 로그 출력 (컴파일러가 제공하는 복사 생성자 사용)
Person(const Person& p) : id(p.id), name(p.name) {
logCopyConstructor(p.name); // 복사 생성자 호출 시 로그 출력
}
// 소멸자
~Person() {
delete[] name;
cout << "Destructor executed, id: " << id << ", name: " << (name ? name : "NULL") << endl;
}
// 이름 변경
void changeName(const char* newName) {
delete[] name; // 기존 메모리 해제
name = new char[strlen(newName) + 1]; // 새로운 메모리 할당
strcpy(name, newName);
cout << "Name changed to: " << name << endl;
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void f(Person p) { // 값에 의한 호출로 객체가 전달될 때, person 객체의 복사 생성자 호출
p.changeName("Kim Young woo");
}
Person g() { // 함수에서 객체를 리턴할 때, mother 객체의 복사본 생성, 복사본의 복사 생성자 호출
Person mother(2, "Hyun So Bin");
return mother;
}
int main() {
/*객체를 초기화할때 복사생성자를 호출한다*/
Person father(1, "Kim Min Soo"); // 객체를 초기화하여 객체가 생성될 때, mother 객체의 복사 생성자 호출
Person mother = father;
/*값에 의한 호출*/
f(father); // father 객체의 복사 생성자 호출
/*함수에서 값을 리턴*/
g();
}
출력 결과:
복사 생성자 실행 Kim Min Soo
복사 생성자 실행 Kim Min Soo
복사 생성자 실행 Hyun So Bin
묵시적 복사 생성자 호출 상황
- 개발자가 명시적으로 복사 생성자를 호출하지 않더라도, 특정 상황에서 컴파일러가 자동으로 복사 생성자를 호출한다.
- 이러한 상황은 다음과 같다:
- **
객체 초기화**: 한 객체를 사용하여 다른 객체를 초기화할 때. - **
값에 의한 호출**: 함수를 호출할 때, 객체가 값으로 전달될 때. - **
객체 반환**: 함수가 객체를 반환할 때.
- **
실습 8-3
클래스 Accumulator는 add() 함수를 통해 계속 값을 누적하는 클래스로서, 다음과 같이 선언된다. Accumulator 클래스를 구현하여 전체 프로그램을 완성하시오.
class Accumulator {
int value;
public:
Accumulator(int value); // 매개변수 value로 멤버 value를 초기화한다.
Accumulator& add(int n); // value에 n을 더해 값을 누적한다.
int get(); // 누적된 값 value를 리턴한다.
};
int main() {
Accumulator acc(10);
acc.add(5).add(6).add(7); // acc의 value 멤버가 28이 된다.
cout << acc.get() << endl; // 28 출력
}
풀이:
//실습 8-3
class Accumulator {
int value;
public:
Accumulator(int value); // 매개변수 value로 멤버 value를 초기화한다.
Accumulator& add(int n); // value에 n을 더해 값을 누적한다.
int get(); // 누적된 값 value를 리턴한다.
};
Accumulator::Accumulator(int value) {
this->value = value;
}
Accumulator& Accumulator::add(int n) {
this->value += n;
return *this;
}
int Accumulator::get() {
return this->value;
}
void ex1031_3() {
Accumulator acc(10);
acc.add(5).add(6).add(7); // acc의 value 멤버가 28이 된다.
cout << acc.get() << endl; // 28 출력
}
실습 8-4 포인터를 이용한 복사 생성자
책의 이름과 가격을 저장하는 다음 Book 클래스이다. Book 클래스의 생성자, 소멸자, set() 함수를 구현하고, 실행 결과를 참조하여 깊은 복사 생성자를 작성하라.
class Book {
char *title; // 제목 문자열
int price; // 가격
public:
Book(char* title, int price);
~Book();
void set(char* title, int price);
void show() { cout << title << ' ' << price << "원" << endl; }
};
int main() {
Book cpp("명품C++", 10000);
Book java = cpp;
java.set("명품자바", 12000);
cpp.show();
java.show();
}
출력 결과:
명품C++ 10000원
명품자바 12000
풀이:
// 실습 8-4
class Book {
char* title; // 제목 문자열
int price; // 가격
public:
Book(char* title, int price); // 그냥 자
Book(Book& obj); // 복사 생성자
~Book();
void set(char* title, int price);
void show() { cout << title << ' ' << price << "원" << endl; }
};
Book::Book(char* title, int price) {
// 클래스 멤버 명이랑 함수 내 지역변수명이랑 같을때 this 포인터 사용
//this->title = title;
//this->price = price;
// 클래스 멤버 지역변수
int length = strlen(title);
this->title = new char[length+1];
this->price = price;
strcpy(this->title, title);
}
Book::Book(Book& obj) {
this->price = obj.price;
int length = strlen(obj.title);
this->title = new char[length + 1];
strcpy(this->title, obj.title);
}
Book::~Book() {
delete[] this->title;
cout << "소멸자" << endl;
}
void Book::set(char* title, int price) {
delete[] this->title;
int length = strlen(title);
this->title = new char[length+1];
strcpy(this->title, title);
this->price = price;
}
void main() {
// Book cpp("명품C++", 10000); // 글자는 고정된 값이기에(상수라 생각하면 됨), 함수쪽이랑
Book cpp((char*) "명품C++", 10000);
Book java = cpp;
java.set((char*) "명품자바", 12000);
cpp.show();
java.show();
}
(추가)
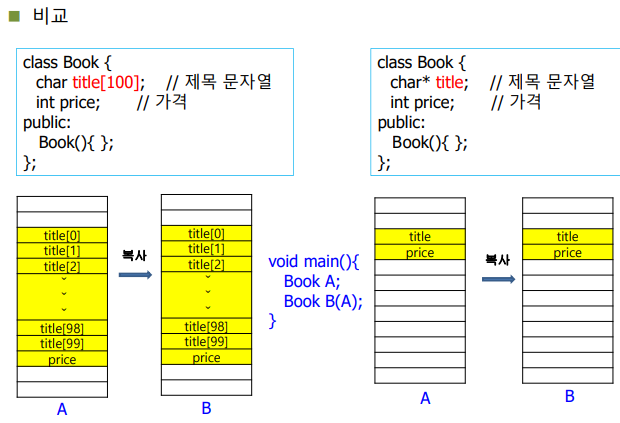
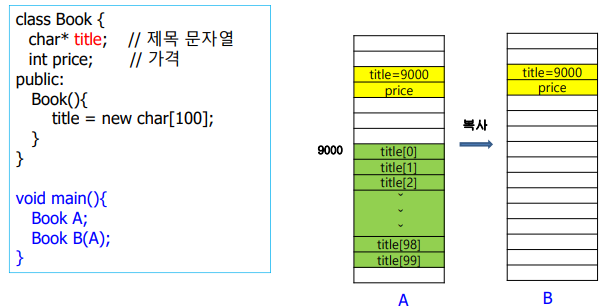
- 배열 멤버 변수의 특징:
- 클래스 내부에서 배열(
char title[100])로 멤버 변수를 선언하면, 객체가 생성될 때 배열 전체가 객체의 메모리 공간에 포함된다. - 배열은 복사 생성자 없이도 객체 복사 시 값 자체가 복사되므로, 깊은 복사를 별도로 구현할 필요가 없다.
- 클래스 내부에서 배열(
- 객체 복사 시 동작:
- 객체를 복사하면 배열의 값(내용)이 메모리의 새로운 공간에 복사된다.
- 이 과정에서 배열의 주소가 서로 다르다:
- 원본 객체와 복사된 객체는 독립적인 배열 메모리를 가지게 된다.
- 따라서, 복사된 객체를 수정하더라도 원본 객체는 영향을 받지 않는다.
- 비교 설명:
- 멤버 변수가 포인터일 경우:
- 얕은 복사가 발생하여 두 객체가 동일한 메모리를 참조하게 된다.
- 이 경우, 깊은 복사 생성자를 명시적으로 구현해야 한다.
- 멤버 변수가 배열일 경우:
- 배열 내용이 새로운 메모리 공간에 복사되므로, 두 객체는 독립적인 메모리를 가진다.
- 복사 생성자를 별도로 작성하지 않아도 안전하게 동작한다.
- 멤버 변수가 포인터일 경우:
즉, 포인터가 없으면 복사생성자를 만들 필요가 없다.
실습 8-5
책의 이름과 가격을 저장하는 다음 Book 클래스이다. Book 클래스의 생성자, 소멸자, set() 함수를 구현하고, 실행 결과를 참조하여 깊은 복사 생성자를 작성하라.
class Book {
char title[100]; // 제목 문자열
int price; // 가격
public:
Book(char* title, int price);
~Book();
void set(char* title, int price);
void show() { cout << title << ' ' << price << "원" << endl; }
};
int main() {
Book cpp("명품C++", 10000);
Book java(cpp);
java.set("명품자바", 12000);
cpp.show();
java.show();
}
출력 결과:
명품C++ 10000원
명품자바 12000원
풀이:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // 문자열 처리 함수 (strcpy) 사용을 위한 헤더
using namespace std;
// Book2 클래스 정의
class Book2
{
char title[100]; // 제목 문자열 (고정 크기 배열)
int price; // 가격
public:
Book2(char *title, int price); // 생성자 선언
~Book2(); // 소멸자 선언
void set(char *title, int price); // 제목과 가격을 수정하는 함수
void show() { cout << title << ' ' << price << "원" << endl; } // 제목과 가격 출력
};
// 생성자 구현
Book2::Book2(char *title, int price)
{
// 제목 문자열 복사
strcpy(this->title, title); // 외부에서 전달된 문자열을 내부 배열에 복사
this->price = price; // 가격을 초기화
}
// 소멸자 구현
Book2::~Book2()
{
// 객체 소멸 시 호출되는 함수
cout << "소멸자" << endl; // 객체가 소멸되었음을 알리기 위한 메시지 출력
}
// set() 함수 구현
void Book2::set(char *title, int price)
{
// 제목과 가격을 수정하는 함수
strcpy(this->title, title); // 제목을 새로운 문자열로 덮어씀
this->price = price; // 가격을 새로운 값으로 설정
}
// main 함수 (ex1104_1)
int ex1104_1()
{
// "명품C++" 문자열과 가격 10000으로 cpp 객체 생성
// 문자열 상수는 `char*`로 캐스팅하여 전달
Book cpp((char *)"명품C++", 10000); // cpp 객체 생성 (생성자 호출)
// cpp 객체를 복사하여 java 객체 생성 (디폴트 복사 생성자 호출)
Book java = cpp;
// java 객체의 제목과 가격 수정
java.set((char *)"명품자바", 12000);
// cpp 객체 정보 출력
cpp.show(); // 출력: 명품C++ 10000원
// java 객체 정보 출력
java.show(); // 출력: 명품자바 12000원
return 0; // 프로그램 종료
}

댓글남기기